- NGOs are critical for social welfare and development in India, registered under various legal structures.
- NGOs can be formed as a Section 8 Company, Society, or Trust, each with specific regulations.
- A Section 8 Company promotes charitable objectives, has limited liability, and no minimum capital requirement.
- A Society requires a minimum of 7 members and is suitable for large memberships.
- A Trust is established by a settlor for societal benefit and can be private or public.
- Tax exemptions for NGOs include 80G and 12A registrations under the Income Tax Act, 1961.
- Compliance with annual filings and audits is essential to maintain NGO status and enjoy benefits.
- NGOs are critical for social welfare and development in India, registered under various legal structures.
- NGOs can be formed as a Section 8 Company, Society, or Trust, each with specific regulations.
- A Section 8 Company promotes charitable objectives, has limited liability, and no minimum capital requirement.
- A Society requires a minimum of 7 members and is suitable for large memberships.
- A Trust is established by a settlor for societal benefit and can be private or public.
- Tax exemptions for NGOs include 80G and 12A registrations under the Income Tax Act, 1961.
- Compliance with annual filings and audits is essential to maintain NGO status and enjoy benefits.
Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs) play a crucial role in social welfare and development. In India, NGOs can be registered under three legal structures:
- Section 8 Company (under the Companies Act, 2013)
- Society (under the Societies Registration Act, 1860)
- Trust (under the Indian Trusts Act, 1882 or relevant state laws)
This guide provides a detailed legal overview of forming an NGO, including legal provisions, documentation, benefits, capital requirements, and income tax exemptions.
Related video:
1. Section 8 Company
A Section 8 Company is a non-profit entity registered under the Companies Act, 2013 that promotes charitable objectives like education, social welfare, art, environment, and research.
Legal Provisions ⚖️
- Governed by Section 8 of the Companies Act, 2013
- Regulated by the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) ️
Benefits
✅ Limited Liability – Members are not personally liable for debts.
✅ No Minimum Capital Requirement – Can be started with any amount.
✅ Better Credibility – More recognized than a Trust or Society.
✅ Eligible for Tax Exemptions – Under Income Tax Act, 1961.
✅ Government Grants & CSR Funding – Eligible for financial support.
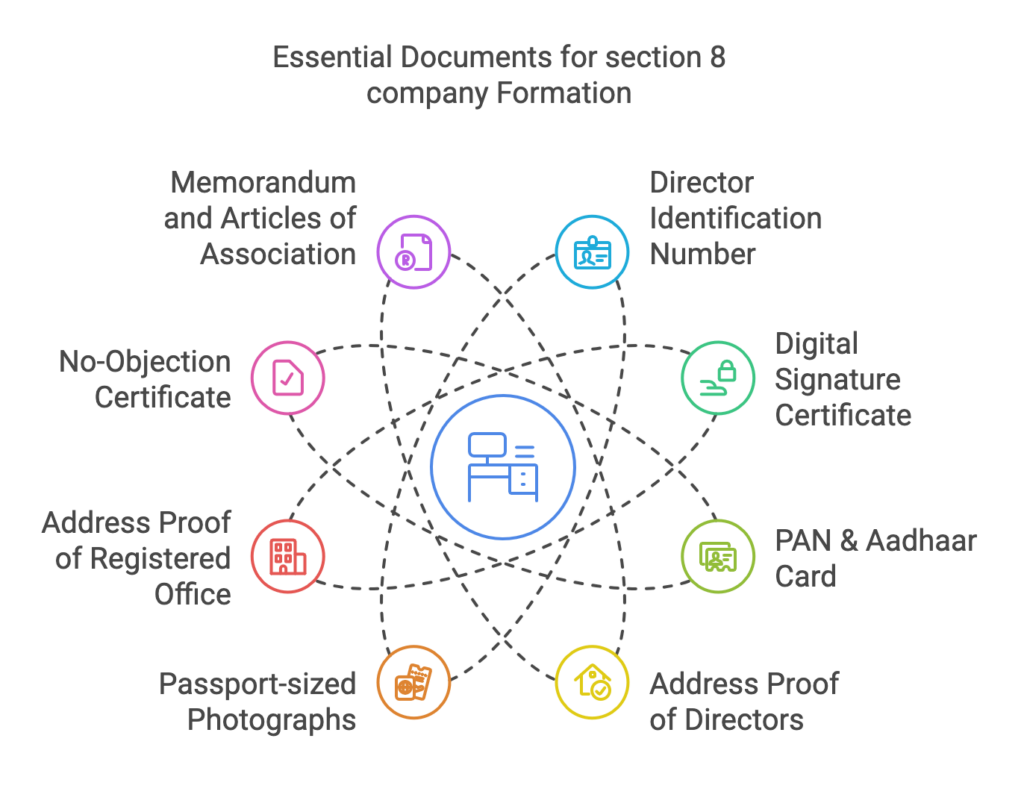
Documents Required
Director Identification Number (DIN) of all directors.
Digital Signature Certificate (DSC) of all directors.
PAN & Aadhaar Card of directors.
Registered Office Address Proof (rent agreement or ownership proof).
No-Objection Certificate (NOC) from the property owner.
Memorandum of Association (MoA) & Articles of Association (AoA).
Capital Requirement & Maintenance Charges
No minimum capital required.
Annual Compliance Costs – ₹10,000 to ₹50,000 depending on filings and audit fees.
Financial Statements & Tax Filings required yearly.
2. Society Registration ️
A Society is a group of individuals coming together for charitable, cultural, religious, or social purposes. It is registered under the Societies Registration Act, 1860.
Legal Provisions ⚖️
- Governed by the Societies Registration Act, 1860
- Requires a minimum of 7 members to form a society
Benefits
✅ No Minimum Capital Requirement
✅ Suitable for Large Memberships
✅ Greater Transparency & Democratic Functioning
✅ Eligible for Government Grants & Foreign Funding (FCRA approval required)
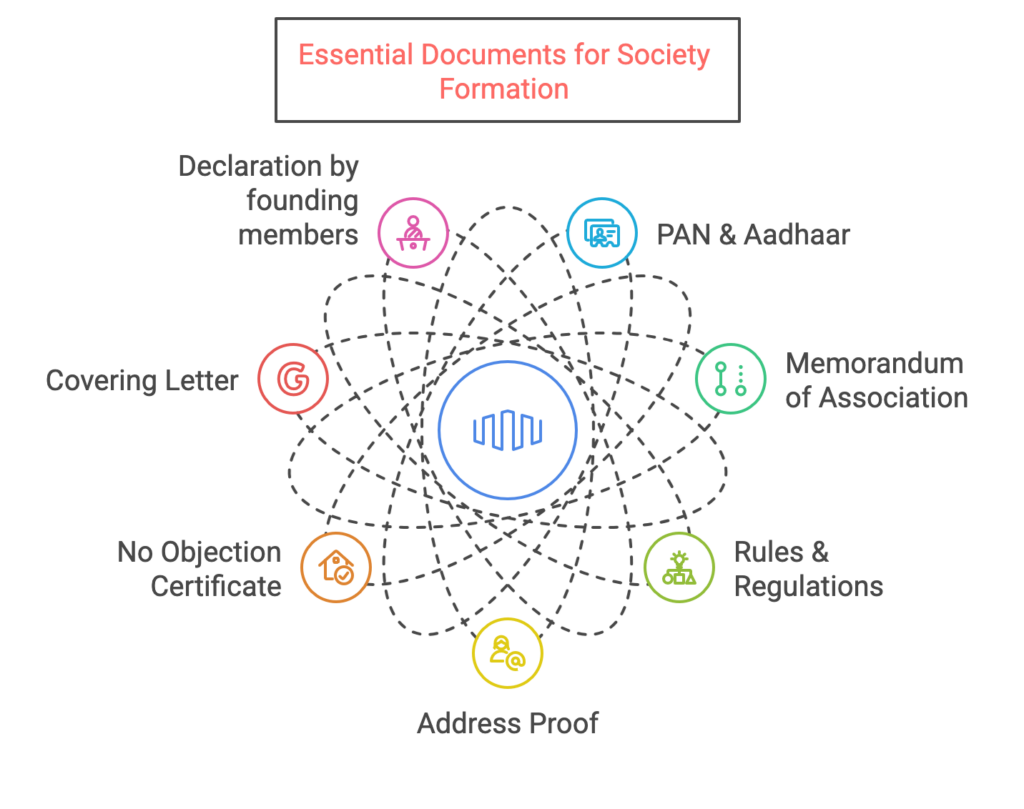
Documents Required
PAN & Aadhaar of Founding Members
Memorandum of Association (MoA) outlining objectives
Rules & Regulations Document
Registered Office Address Proof
No Objection Certificate (NOC) from the Landlord
Declaration Signed by the President of the Society
Annual Maintenance & Compliance
Annual Report Filing with the Registrar.
Proper Accounting & Auditing Required.
Compliance Costs:₹5,000 – ₹20,000 per year.
3. Trust Formation
A Trust is an entity where a settlor transfers property to trustees for the benefit of society. It can be registered as a Private Trust or a Public Charitable Trust.
Legal Provisions ⚖️
- Indian Trusts Act, 1882 (for Private Trusts)
- Public Trusts Act (State-Specific for Charitable Trusts)
- Requires Minimum Two Trustees (no upper limit)
Benefits
✅ Easy & Cost-Effective Registration
✅ Ideal for Religious, Educational & Welfare Activities
✅ Trust Properties Are Legally Protected
✅ Eligible for 12A & 80G Tax Exemptions
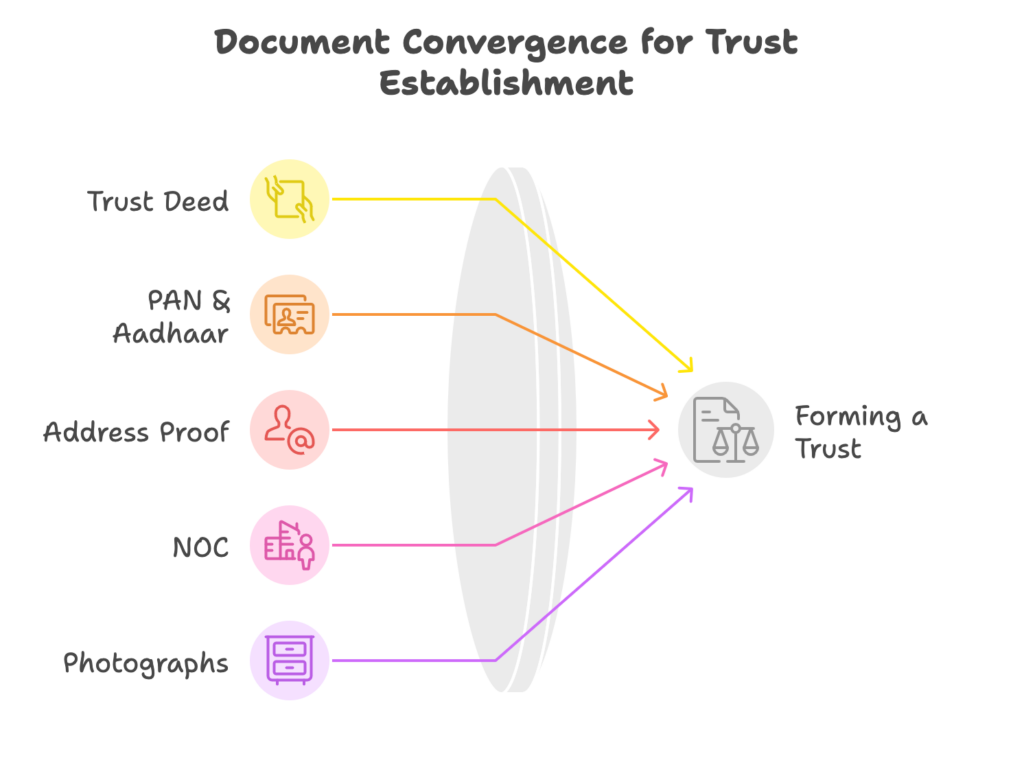
Documents Required
Trust Deed (on Non-Judicial Stamp Paper)
PAN & Aadhaar of Settlor & Trustees
Registered Office Address Proof
NOC from the Property Owner
Photographs of Trustees
Annual Maintenance & Compliance
Financial Statements & Audit Reports Required
Income Tax Returns (ITR) Filing Mandatory
Compliance Costs: ₹5,000 – ₹30,000 per year.
Income Tax Exemptions for NGOs
To enjoy tax benefits, NGOs must obtain the following under the Income Tax Act, 1961:
✅ 80G Certificate – Allows donors to claim tax deductions.
✅ 12A Registration – Exempts NGO from paying income tax.
✅ FCRA Registration (For foreign contributions) – Required under Foreign Contribution Regulation Act, 2010.
Process for Tax Exemptions
1️⃣ Form 10A – For 12A Registration (via the Income Tax e-filing portal).
2️⃣ Form 10G – For 80G Approval.
3️⃣ Submission of Audited Financials, PAN, and Registration Certificate.
4️⃣ Approval from the Commissioner of Income Tax (Exemptions).
5️⃣ Issuance of 80G & 12A Certificates ✅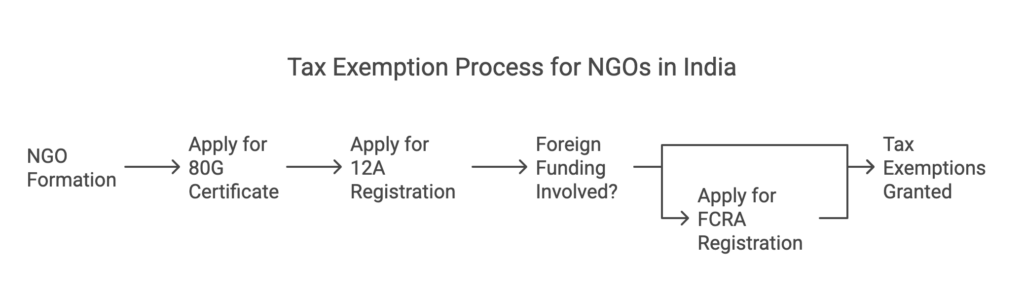
Let Us Help You Register Your NGO!
Need expert guidance for NGO registration? Our legal experts & consultants are here to assist you with seamless registration, documentation, compliance & tax exemptions. Contact us today and start your social impact journeyhassle-free!
Email Us: [email protected]
Call Us:(+91) 890 222 4444/8250 422 880
Visit Us: https://patraslawchambers.com/ngo-registration-cheapest-cost/